
Kevlar® soft-body armor design requirement for LEO
Soft-body Armor Analysis and Design for Law Enforcement Officer (Part 1)
This article is part 1 of my portfolio specifically about the Kevlar and the material science behind such soft-body armor.
Read Part 2: Soft-body Armor Analysis
Glossary#
Crystallinity: The degree of structural order in a solid where atoms or molecules are arranged in a regular, periodic manner. It has a big influence on hardness, density, transparency and diffusion.
Liquid Crystalline: state of matter which has properties between those of conventional liquids and those of solid crystals. Indication of Short Range order (Little Repeating order) and Long Range order only in small volumes.
Anisotropy: The property of being directionally dependent, which implies different properties in different directions.
Point Defect: Where an atom is missing or is in an irregular place in the lattice structure. Includes: self-interstitial atoms, interstitial impurity atoms, substitutional atoms and vacancies.
Thermosetting Polymer: A polymer that is irreversibly hardened by curing from a soft solid or viscous liquid prepolymer or resin.
The needs for Soft-body Armor#
Nowadays, protection clothes are widely used not only for army but also for civilians and it has significantly contributed to the safety of human. In military, protection clothes, or also called bullet-proof vest is used for soldier which can reduces the force of a bullet in order to minimize the damage a ballistic projectile can cause. Thanks to protection clothes, our lives have advanced in many positive ways.
This research aims to analyze the commercial use of aramid fiber (trademark name is Kevlar®) in ballistic-propellant armor specifically designed for Law Enforcement Officer who have to face potential confrontation threats with firearm on a daily basic.
Law Enforcement Armor Specs#
In order to prevent casualties because of high velocity ammunition and increase the movement ability for law enforcement officers, a lightweight ballistic-propellant material has been the main focus of manufacturers. The determinants can be listed solely in these categories:
- High tensile strength to resists impact
Energy absorption capacity and impact load resistance are primarily the main concerns when dealing with ballistic resistant clothes. A ballistic-propellant armor should be able to resist the kinetic energy of a relatively low impact bullet (velocity < 600𝑚/𝑠) as well as its fragmentation which is Type II based on the NIJ Standard of the US* Department of Justice* for ballistic resistance of body armor.
- Low density to decrease total body weight and maximize the mobility
Law enforcement officers in pursuing criminals typically on foot which requires the material to have low density in order to cut down the total carrying masses or saving up for another layer to enhance the resistances.
- High Young’s Modulus to prevent damages
High Young’s modulus is an extreme factor for energy absorption feature because it indicates the capability of material to deform elastically before permanently broken and since the vest covering within millimeters around the body, the modulus should be large to maximize the impact resistance through stacked layers.
- High Extensibility
Similarly, the elongation at break should be high to maximize the ability of each layer to dissipate the penetrating energy because energy absorption will cause plastic deformation (also permanent) until failure.
- Low thermal conductivity to resists exothermic related impacts
The material should have low thermal conductivity in order to marginalize the explosion impacts since law enforcement officers have constantly facing fire related hostility such as dealing with explosive firearms and especially fire hazardous situation.
Material Specifications#
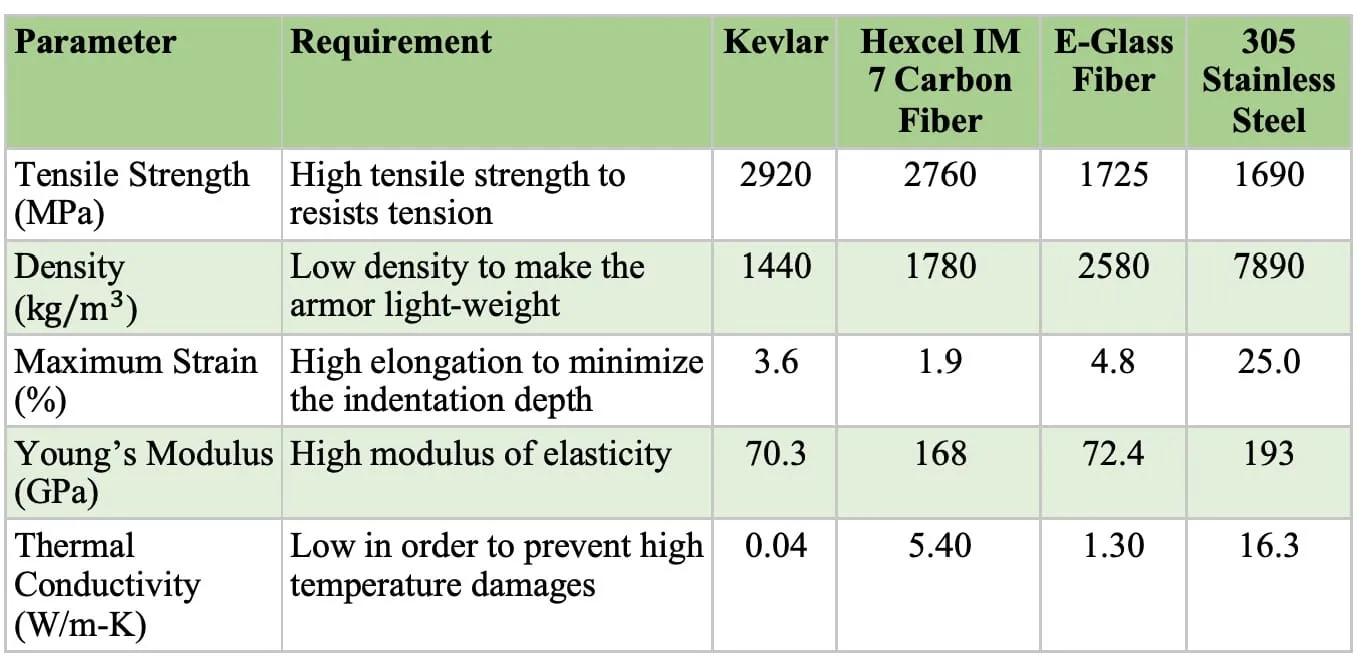 Table 1: Comparison between materials for soft body armor
Table 1: Comparison between materials for soft body armor
It can be seen that 305 Stainless Steel soon be ruled due to the massive density and thermal conductivity despite being highly ductile and stiffer the most. *E-Glass fiber *seemingly good at extensibility but outweighed amongst fiber and has the least tensile strength. Hexcel IM 7 Carbon Fiber and Kevlar Fiber are the two ideal materials left, having high modulus and low strain indicates the highly stiffness of Hexcel IM 7 Carbon whereas Kevlar still in the lead in term of strength to weight ratio.
Conclusively, Kevlar Fiber with the extraordinary strength to weight ratio, low density and relatively high strain as feature for lightweight and extensibility, superior thermal stability and comply with other requirements, is the selected material for further examination.
Kevlar Properties#
Further examination of Kevlar Fiber properties indicate that
Mechanical Properties#
- Tensile strength
The tensile strength of Kevlar as of 2920 MPa is highest amongst fabric materials whereas being the most light-weight material (Table 1).
- Extensibility
The maximum strain measured in Kevlar is 3.6% which is relatively high for fibers as compare to Hexcel IM 7 Carbon fiber and E-glass fiber.
- Young’s modulus
The low modulus of elasticity at 70.3GPa shows that Kevlar is easy to deform permanently compare to other fiber (Hexcel IM 7) but it also means that Kevlar has lower stiffness and more flexible (Table 1).
- Density
Kevlar is relatively low in comparison with other common fabric materials with 1440 kg/ which remarkably light-weight compared to 305 stainless steel whilst twice as strong (Table 1).
Thermal Properties#
Thermal conductivity of Kevlar is impressively low in comparison with only 0.04 W/m-k which demonstrates the thermal stability of it. In the low-temperature range, aramid fibers retain their properties even at −70°C .
Other Properties#
Kevlar has no metallic properties which cannot interfere with electronic devices . This is a dramatic improvement compared to other ballistic-propellant armor made of stainless steel or other metal alloys. Thus, prevent jamming or disconnection when communicate via radio receivers.
Aramid Fiber Composition#
Atomic Arrangement#
Aramid Fiber is a composition defined as poly para-phenylene terephthalamide (PPTA). Each PPTA monomer contains 14 carbon atoms, 2 nitrogen atoms, 2 oxygen atoms, and 10 hydrogen atoms in total of 28 atoms . That is, the molecular structure has two aromatic rings() and two amide groups(CO-NH) join at carbon 1 and 4 (para oriented) (See Table 2).
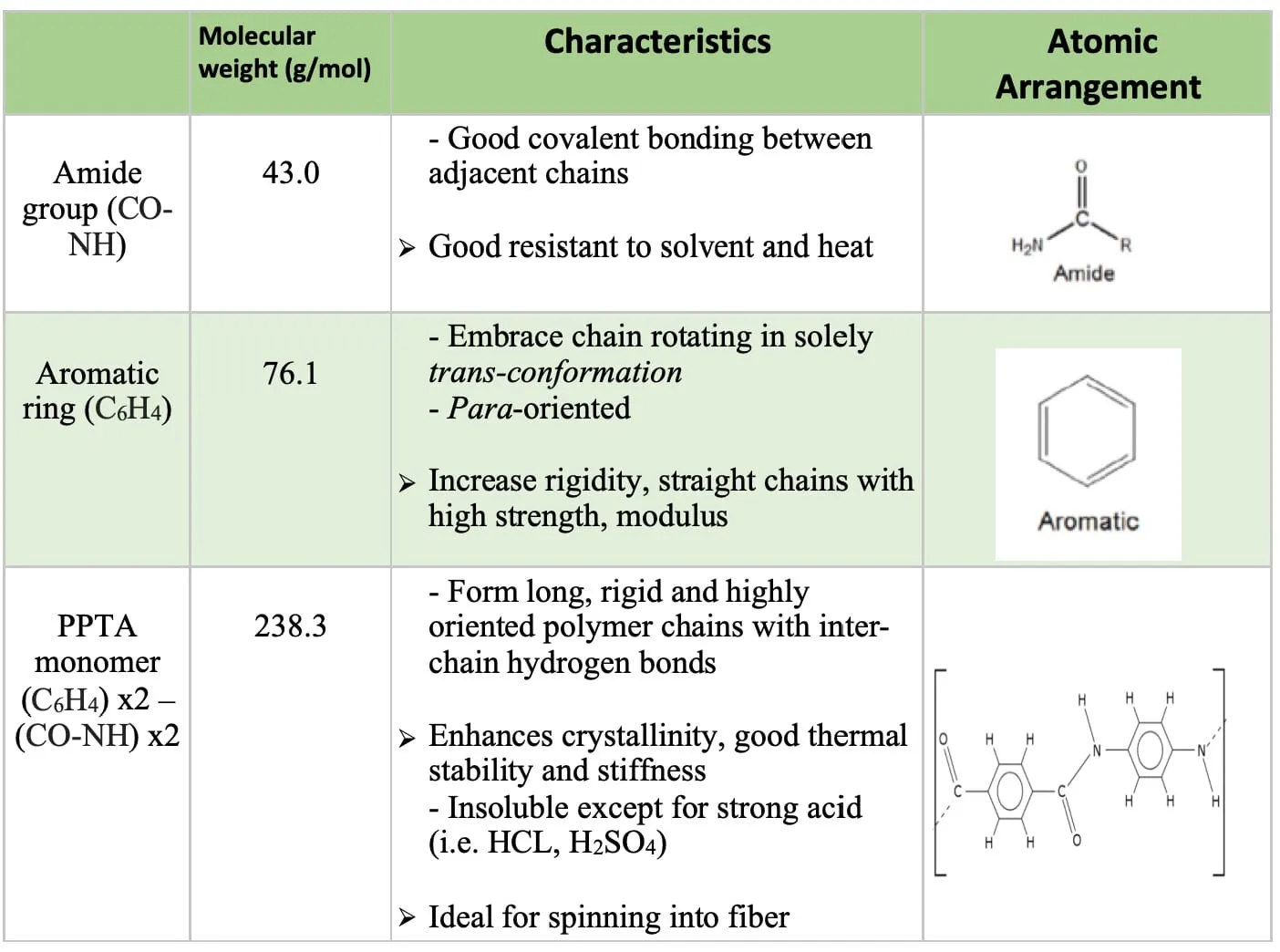 Table 2: Chemical composition & Atomic arrangement of Kevlar® Aramid Fiber
Table 2: Chemical composition & Atomic arrangement of Kevlar® Aramid Fiber
Conformational Isomerism#
In trans-conformation, where the hydrocarbon groups are in the opposite side of the amide bond, causes the chain stretched out in an extremely straight manner and binds with other similar chains .
On the other hand, in cis-conformation, hydrocarbon groups are in the same side of the amide bond, the conformation hardly occurs because the aromatic rings hinder the molecule motion which prevent the chains from rotating and twisting around to conform.
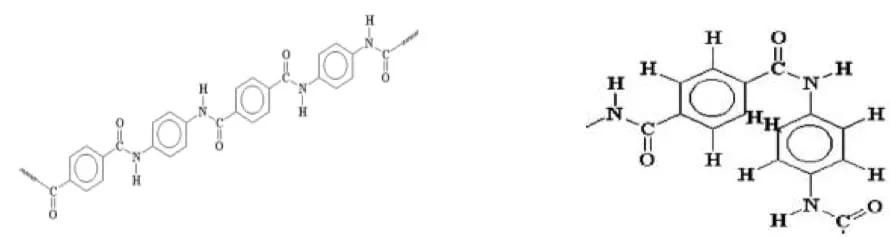 Trans-conformation (Left) and Hindrance in cis-conformation (Right)
Trans-conformation (Left) and Hindrance in cis-conformation (Right)
As a result, PPTA conformation occurs almost entirely in trans-conformation forming a radial orientation which is the primary factor to make strong, stiff fiber since it long, straight and fully extended chains pack perfectly fit into the crystalline form.
Moreover, the high degree of chain alignment combined with hydrogen bonded amide increase the dispersion forces from stacking interaction between adjacent sheets, thus strengthening further resistance capacity as well as the thermal stability.
Microstructure#
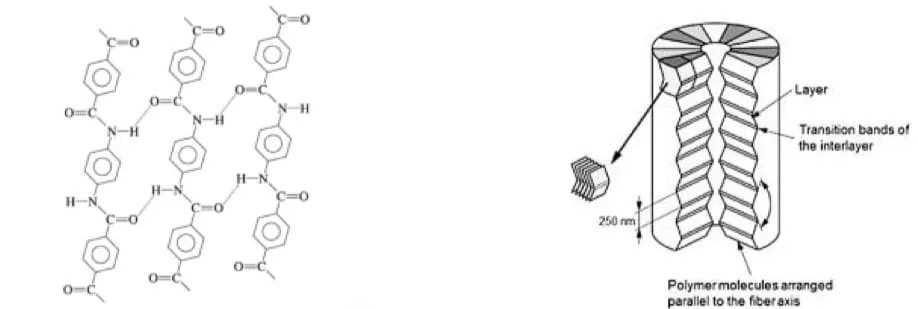
At least 85% of the amide groups enable the chain attaches directly to two aromatic rings via covalent bonding between CO and NH groups. On inter-chain level, the amide group exhibits hydrogen bonding to bind adjacent chains together which forming a plat sheet and stacked upon each other as described in pleat structure in the longitudinal direction of fiber axis.
 Hydrogen bonded sheet by cross-linking (Left) and Pleat Structure (Right)
Hydrogen bonded sheet by cross-linking (Left) and Pleat Structure (Right)
Crystal Structure#
In the solute stages (Dope preparation), dopes exhibit liquid-crystalline properties since it has liquid crystal regions . The crystalline regions have the structure of monoclinic with pseudo-orthorhombic symmetry which indicates three unequal axes (a ≠ b ≠ c) at right angle (𝛼 = 𝛽 = γ = 90 °) . Furthermore, the three lattice parameters in the unit cell measured at a: b: c = 0.787:0.519:1.29 nm.
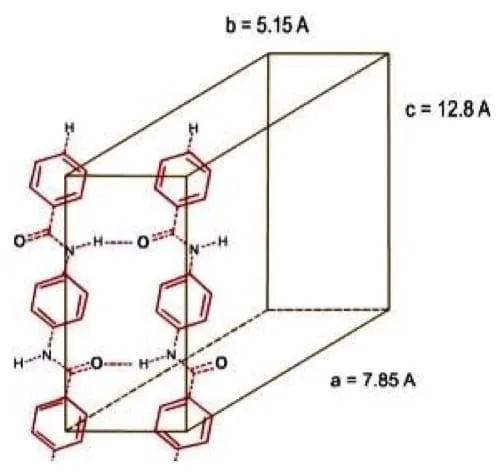 Crystal structure in solution
Crystal structure in solution
The alignment of PPTA is defined by the angle between the amide group and the fiber axis (c-axis) which indicates the mis-orientation of chains with respect to fiber axis and has value of 12 °± 0.2. Thus, this angle contributes to predict the crystallinity and modulus of a fiber and can be treated for improvement. More on Defects and Strengthening mechanism.